Over the past four decades, it was theorised that Biomagnetic pair therapy helps neutralise the body’s pH levels, building a hostile environment to pathogens. Recent empirical evidence has established that static magnetic fields (magnets therapists use in Biomagnetism sessions) provide a myriad of mechanisms of action. One relevant mechanism of action resides in the influence of biological processes at the cellular and molecular levels [1]. Static magnetic fields straighten the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane [Figure 1]. As a consequence, transmembrane proteins change conformation, allowing them to become more efficient (more active) in transporting ions through the phospholipid cell membrane [Figure 2].
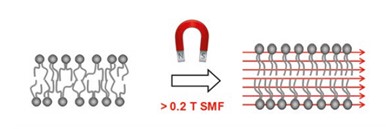
Figure 1
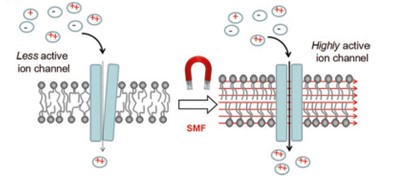
Figure 2
This efficiency in the transmembrane proteins is highly relevant, especially in calcium channels which control the gene expression of cytokines such as Interleukin 6 [2]. Research evidence has demonstrated that Interleukin 6 is involved in immune response [3,4], tissue regeneration [5,6,7] and the formation of the intestinal epithelial barrier [8]. The formation of the epithelial barrier in the intestines is crucial for maintaining gut homeostasis and protecting the body from harmful substances while allowing the absorption of nutrients [9].
Learn about other mechanisms of action
References
-
Zhang X, Yarema K, Xu A, Zhang X, Yarema K, Xu A. Molecular Mechanisms for Electromagnetic Field Biosensing. Biological Effects of Static Magnetic Fields. 2017:51-79.
-
Wang Z, Sarje A, Che P-L, Yarema KJ. Moderate strength (0.23–0.28 T) static magnetic fields (SMF) modulate signaling and differentiation in human embryonic cells. BMC genomics. 2009;10:1-23.
-
Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(10):a016295.
-
Hoge J, Yan I, Jänner N, Schumacher V, Chalaris A, Steinmetz OM, et al. IL-6 controls the innate immune response against Listeria monocytogenes via classical IL-6 signaling. The Journal of Immunology. 2013;190(2):703-11.
-
Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, Poli V, et al. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science. 1996;274(5291):1379-83.
-
Galun E, Zeira E, Pappo O, Peters M, Rose-John S. Liver regeneration induced by a designer human IL‐6/sIL‐6R fusion protein reverses severe hepatocellular injury. The FASEB Journal. 2000;14(13):1979-87.
-
Kuhn KA, Manieri NA, Liu T-C, Stappenbeck TS. IL-6 stimulates intestinal epithelial proliferation and repair after injury. PloS one. 2014;9(12):e114195.
-
Kuhn KA, Schulz HM, Regner EH, Severs EL, Hendrickson JD, Mehta G, et al. Bacteroidales recruit IL-6-producing intraepithelial lymphocytes in the colon to promote barrier integrity. Mucosal Immunology. 2018;11(2):357-68
-
Rios-Arce ND, Collins FL, Schepper JD, Steury MD, Raehtz S, Mallin H, et al. Epithelial Barrier Function in Gut-Bone Signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1033:151-83.
